Le caratteristiche dei liposomi li rendono adatti ad essere utilizzati in diversi campi di applicazione, ne sono un esempio il campo farmaceutico, medico, cosmetico, nutraceutico e alimentare.
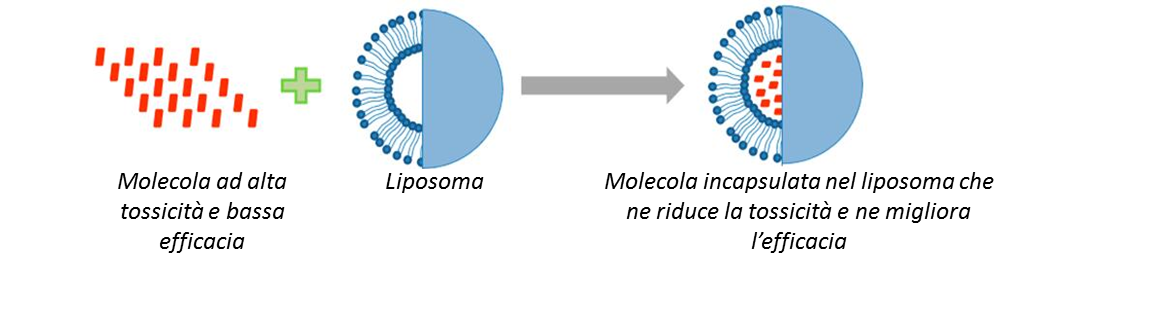
In campo medico i liposomi sono utilizzati per il rilascio controllato di farmaci al fine di potenziare le molecole terapeutiche, mantenendole disponibili per il tempo necessario e in prossimità di tessuti/cellule. Nella terapia genetica sono stati sviluppati farmaci a base di acido nucleico (NABD) e i liposomi risultano i veicoli più adatti per il trasporto di questi farmaci, limitando la loro tossicità e assicurandone il rilascio e l’espressione nei tessuti target.
 Nel contesto cosmetico, dove la nanotecnologia è considerata uno strumento attrattivo e innovativo, i nanoliposomi, creati attraverso la tecnica in continuo SMF-Simil Microfluidica ideata dallo spin-off, sono ideali per la formulazione di creme anti-età, creme idratanti, lozioni solari, maschere di bellezza per il viso oppure soluzioni per il trattamento della caduta dei capelli.
Nel contesto cosmetico, dove la nanotecnologia è considerata uno strumento attrattivo e innovativo, i nanoliposomi, creati attraverso la tecnica in continuo SMF-Simil Microfluidica ideata dallo spin-off, sono ideali per la formulazione di creme anti-età, creme idratanti, lozioni solari, maschere di bellezza per il viso oppure soluzioni per il trattamento della caduta dei capelli.
Nel settore alimentare invece i liposomi hanno un grande potenziale come materiali “contenitori” per preservare molti ingredienti bioattivi, inclusi i composti che sono poco solubili in acqua, vitamine, proteine, peptidi.
Di seguito alcune delle pubblicazioni sull’argomento realizzate dai componenti di Eng4life.
2021
Bochicchio, Sabrina; Dalmoro, Annalisa; Lamberti, Gaetano; Barba, Anna Angela
Nanoliposomi in cosmetica e cosmeceutica Journal Article
In: ICF – Rivista dell’industria chimica e farmaceutica, vol. Febbraio/Marzo 2021, no 1, pp. 66-71, 2021.
@article{Bochicchio2021,
title = {Nanoliposomi in cosmetica e cosmeceutica},
author = {Sabrina Bochicchio and Annalisa Dalmoro and Gaetano Lamberti and Anna Angela Barba},
url = {https://interprogettied.com/icf-rivista-dellindustria-chimica-e-farmaceutica-n1-febbraio-marzo-2021/},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-03-26},
journal = {ICF – Rivista dell’industria chimica e farmaceutica},
volume = {Febbraio/Marzo 2021},
number = {1},
pages = {66-71},
abstract = {L’uso di nanotecnologie per potenziare le performance dei prodotti cosmetici e cosmeceutici ha consentito una rapida crescita di questo settore industriale. Registrano un’ampia richiesta di mercato i nanocosmeceutici per la cura della pelle, dei capelli, delle unghie e delle labbra, oltre a quelli per contrastare rughe, fotoinvecchiamento, iperpigmentazione, forfora e danni ai capelli.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2020
Simone, Veronica De; Dalmoro, Annalisa; Bochicchio, Sabrina; Caccavo, Diego; Lamberti, Gaetano; Bertoncin, Paolo; Barba, Anna Angela
Nanoliposomes in polymeric granules: Novel process strategy to produce stable and versatile delivery systems Journal Article
In: Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, vol. 59, pp. 7, 2020.
@article{Simone}2020,
title = {Nanoliposomes in polymeric granules: Novel process strategy to produce stable and versatile delivery systems},
author = {Veronica {De Simone} and Annalisa Dalmoro and Sabrina Bochicchio and Diego Caccavo and Gaetano Lamberti and Paolo Bertoncin and Anna Angela Barba},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1773224720311679?via%3Dihub},
doi = {10.1016/j.jddst.2020.101878},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-07-09},
journal = {Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology},
volume = {59},
pages = {7},
abstract = {Liposomes, due to their mimetic cellular composition, are gaining great attention as release systems for lipophilic and hydrophilic molecules. However, liposomes can present a high tendency to degrade and aggregate into biological fluids and under storage conditions. To overcome these limitations, in this work, a stabilizing strategy consisting in liposomes incorporation into polymeric granules was studied. Wet granulation was adopted to produce granules of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) and liposomal suspensions were used as the binder phase. In particular, in this study, three different percentages of liposome load in HPMC granules were investigated (1%, 5% and 10% w/w) focusing the attention on several relevant technological characteristics of the achieved solid particulates: size, flow index, mechanical strength (granules without liposomal inclusions were used as a control). Morphological observations (by TEM) confirmed the presence of intact liposomes in dry HPMC granules; moreover, it was found that the binder phase with the lower liposome concentrations (1%, 5%) did not significantly affect size, flowability and hardness of the lipid-polymer granules. Instead, the granules containing the highest percentage of liposomes (10% w/w) have larger dimensions, harder structure and reduced flowability. Therefore, the followed process strategy, under liposomal concentration restrictions, allowed to obtain both the liposomes stabilization, a not trivial technological issue, and the production of particulates with good solid state properties, useful as a versatile dosage form (lipid carriers in polymer carriers).},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Bochicchio, Sabrina; Dalmoro, Annalisa; Simone, Veronica De; Bertoncin, Paolo; Lamberti, Gaetano; Barba, Anna Angela
Simil-Microfluidic Nanotechnology in Manufacturing of Liposomes as Hydrophobic Antioxidants Skin Release Systems Journal Article
In: Cosmetics, vol. 7, no 22, pp. 13, 2020.
@article{Bochicchio2020,
title = {Simil-Microfluidic Nanotechnology in Manufacturing of Liposomes as Hydrophobic Antioxidants Skin Release Systems},
author = {Sabrina Bochicchio and Annalisa Dalmoro and Veronica De Simone and Paolo Bertoncin and Gaetano Lamberti and Anna Angela Barba},
editor = {MDPI},
url = {https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9284/7/2/22/pdf},
doi = {10.3390/cosmetics7020022},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-04-03},
journal = {Cosmetics},
volume = {7},
number = {22},
pages = {13},
abstract = {Novel nanotechnologies represent the most attractive and innovative tools to date exploited by cosmetic companies to improve the effectiveness of their formulations. In this context, nanoliposomes have had a great impact in topical preparations and dermocosmetics, allowing the transcutaneous penetration and absorption of several active ingredients and improving the stability of sensitive molecules. Despite the recent boom of this class of delivery systems, their industrial production is still limited by the lack of easily scalable production techniques. In this work, nanoliposomes for the topical administration of vitamin D3, K2, E, and curcumin, molecules with high antioxidant and skin curative properties but unstable and poorly absorbable, were produced through a novel simil-microfluidic technique. The developed high-yield semi continuous method is proposed as an alternative to face the problems linked with low productive conventional methods in order to produce antioxidant formulations with improved features. The novel technique has allowed to obtain a massive production of stable antioxidant vesicles of an 84–145 nm size range, negatively charged, and characterized by high loads and encapsulation efficiencies. The obtained products as well as the developed high-performance technology make the achieved formulations very interesting for potential topical applications in the cosmetics/cosmeceutical field. },
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2019
Barba, Anna Angela; Bochicchio, Sabrina; Dalmoro, Annalisa; Lamberti, Gaetano
Lipid Delivery Systems for Nucleic-Acid-Based-Drugs: From Production to Clinical Applications Journal Article
In: Pharmaceutics, vol. 11, no 360, 2019.
@article{Barba2019b,
title = {Lipid Delivery Systems for Nucleic-Acid-Based-Drugs: From Production to Clinical Applications},
author = {Anna Angela Barba and Sabrina Bochicchio and Annalisa Dalmoro and Gaetano Lamberti},
url = {https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4923/11/8/360},
doi = {10.3390/pharmaceutics11080360},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-07-24},
journal = {Pharmaceutics},
volume = {11},
number = {360},
abstract = {In the last years the rapid development of Nucleic Acid Based Drugs (NABDs) to be used in gene therapy has had a great impact in the medical field, holding enormous promise, becoming “the latest generation medicine” with the first ever siRNA-lipid based formulation approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for human use, and currently on the market under the trade name Onpattro™. The growth of such powerful biologic therapeutics has gone hand in hand with the progress in delivery systems technology, which is absolutely required to improve their safety and effectiveness. Lipid carrier systems, particularly liposomes, have been proven to be the most suitable vehicles meeting NABDs requirements in the medical healthcare framework, limiting their toxicity, and ensuring their delivery and expression into the target tissues. In this review, after a description of the several kinds of liposomes structures and formulations used for in vitro or in vivo NABDs delivery, the broad range of siRNA-liposomes production techniques are discussed in the light of the latest technological progresses. Then, the current status of siRNA-lipid delivery systems in clinical trials is addressed, offering an updated overview on the clinical goals and the next challenges of this new class of therapeutics which will soon replace traditional drugs},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}